ARTHROSCOPIC SURGERY
- /ARTHROSCOPIC SURGERY
Knee Arthoroscopy
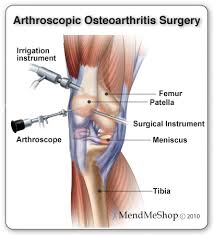
Recent technical advancement allows is to do key-hole surgery. Knee surgery done with the help of arthroscope and camera is known as knee arthroscopy. The main implication is in the sports injury surgeries. In this surgery, two or three single stitch incisions are taken. A small camera called an arthroscope is inserted into the knee joint and the picture is seen on a big video monitor outsideThe whole surgery is done looking at the monitor while manoeuvring the instruments inside the joint. This enables the surgeon to operate through a small incision. Advantages being quick and early recovery, cosmetically better accepted. While the knee is the joint most often viewed and operated using the arthroscope, other joints such as the shoulder, elbow, ankle, hip and wrist can also be viewed using this instrument
Parts of the joint include –
Ligaments: There are two ligaments in the joints and two ligaments outside the joints.
Inside the joint are the cruciate ligaments. Depending on the attachments they are named as Anterior cruciate (ACL) and Posterior cruciate ligaments (PCL). They cross each other to form X. These ligaments give stability to the joint in anteroposterior plane.
Two ligaments are outside the joint. These are collateral ligaments, medial collateral on the medial side and lateral collateral on the lateral side.
The direction of movement of the bones is controlled by the ligaments and the muscles make the joint move.
Meniscus – These are two wedge-shaped rubbery pieces in between the bony ends. Act as filler, the shock absorber of the joint. They are important as a cushion and their loss contributes to the early wear and tear of the joint.
Articular cartilage– The bone ends are covered with a smooth cartilage, hyaline cartilage. Thus the smooth gliding of the joint is in between cartilage over cartilage.
Synovium – This is the lining of the joint. It secretes lubricating fluid inside which help the smooth gliding of the joint. It also nourishes the cartilage. Normally there is around 3 to 5 ml fluid inside our joint.
Muscles – Major muscle groups are quadriceps and hamstring.
Stability of the knee joint is a function of intraarticular and extraarticular ligaments and both these muscle groups.
Indication of knee arthroscopy surgery -
Arthroscopy surgery is indicated mainly in ligament injury and sports injury. Knee arthroscopy may help to relieve painful symptoms of many problems that damage the cartilage surfaces and other soft tissues surrounding the joint.
ACL rupture: ACL reconstruction is one of the most common indications for knee arthroscopy. Because of the increased rate of road traffic accidents the incidence of ACL rupture is also increased.
Meniscal tear: Meniscus is ruptured when there is the twisting force to the joint. The meniscus gets trapped in between the two bones and torn with further force. Today we try to preserve and repair the meniscus as far as possible. If it is irreparable then partial meniscectomy and balancing is done
PCL rupture: It is another important ligament in our body. It can be performed arthroscopically. Many times it gets avulsed with a piece of bone known as PCL avulsion and can be fixed with the small incision.
Combine ligament injury: Many times in a road traffic accident the velocity of injury is so high that more than one ligament with or without the meniscus may get torn. Such is the grievous injuries which need a very systematic approach and management. It may take many months to get back to normal but the patient can be back to almost pre-injury status.
Patellofemoral joint: It is a frequent source of problems. Smoothening of patella undersurface cartilage is known as Chondromalacia Patella. When the patella does not slide in proper line on the femur it is known as Patella Maltracking or ELPS. The third is recurrent patella dislocation. In all these pathologies variety of stabilization procedures are recommended which can be done arthroscopically.
Early arthritis: In the early stages of osteoarthritis the articular cartilage damage can be repaired and stabilized. Sometimes unstable flaps can be removed and micro- drilling or microfracture is done to the underlying bone to encourage new cartilage to form.
Synovitis: In case of severe inflammation in active arthritis or in other causes of inflammatory pathologies subtotal synovectomy can be done arthroscopically. The inflamed synovium is removed arthroscopically.
Loose body: Bone, cartilage or any other loose tissue can be removed to prevent ongoing damage to the knee.
Biopsy: Biopsy is indicated in the variety of pathologies and diagnosis need to be established. In these cases, an arthroscopic biopsy can be a minimal damage approach.
Procedure -
Usually, two or three stan incisions are taken which are known as portals. Through one portal an arthroscope and camera are introduced. This portal is known as viewing portal. Another portal is used for the introducing the instruments. This is known as instrument portal
The inside picture is seen on a big monitor/TV. Whole surgery is done looking at the monitor while manoeuvring the instruments inside the joint.
Varieties of instruments are available to do the surgery. A power shaver is used to shave off all the debris and synovium which is essential to remove
Many more punches and bitters are required to trim the torn portion of the meniscus and balance it.
In many cases, special devices are used to anchor stitches into bone.
Complications -
Complications are few but can occur after an arthroscopic surgery.
Possible complications include
Infection: As true with any of the surgery infection can occur even in this surgery. Every single precaution is taken at our centre to avoid the infection. Operation room infrastructure, OR manners and judicious use of disposables are essential to keep the infection rate to the minimum. Patient pre- surgery immune status is also very important and can influence the outcome.
Stiffness: Outcome of this surgery depends on a lot more on the rehabilitation protocol and how sincerely you do the exercises. But still, sometimes some amount of stiffness may result.
DVT or blood clot: The rate of DVT is much less with arthroscopic surgery but still it can occur.
Physiotherapy: As I said before the success of these surgeries depends on lot more on how sincerely you follow the exercise protocol.
Rehabilitation protocol is very specific and fixed for different surgery. The patient should not do the exercise which is not been told to do. Same time patient should do all the exercise which are a must. This will restore motion and strengthen the muscles of your leg and knee.